
Rising Energy Prices: What Actually Reduces Bills (And What Just Sounds Good)
- Technical review: Thomas Jevons (Head of Training, 20+ years)
- Employability review: Joshua Jarvis (Placement Manager)
- Editorial review: Jessica Gilbert (Marketing Editorial Team)
- Last reviewed:
- Changes: Updated for January 2026 price cap (£1,758), Warm Homes Plan details, and retrofit electrician demand data
Energy bills are staying high. The January 2026 Ofgem price cap sits at £1,758 annually for a typical household, barely changed from previous quarters despite wholesale gas prices softening since February 2025.
The 2022-2023 crisis peaked at £4,279 in January 2023. We’ve come down from that, but we’re not returning to pre-crisis levels. Why? Because while wholesale gas prices drove the spike, the current floor is set by network upgrade costs, policy levies, and infrastructure investment for electrification.
This creates two realities. First, simple switching between suppliers saves minimal amounts (£50-£100 at most) because the price cap limits variation. Second, meaningful bill reduction requires structural changes to how your home uses energy, which often involves electrical work.
That’s where understanding what actually works, what delivers genuine payback, and where electricians add value versus where they’re unnecessary becomes critical. Because there’s plenty of noise about “energy-saving” products and “smart” solutions that deliver minimal returns, alongside legitimate measures that genuinely cut costs.
This isn’t about switching tariffs or turning your thermostat down 1°C (though that helps). It’s about understanding the difference between marginal gains and structural improvements, realistic payback periods for major investments, and why electricians are increasingly essential for energy efficiency rather than just fixing broken sockets.
Why UK Energy Bills Rose (And Why They're Staying High)
Understanding what drove prices up explains why they’re not coming back down fully.
The 2022-2023 crisis (what happened):
Global wholesale gas prices spiked due to post-Covid demand recovery and geopolitical supply disruptions. UK’s heavy reliance on gas for both heating and electricity generation meant wholesale volatility hit retail prices hard. Ofgem’s price cap adjusted quarterly, passing increases through to households. April 2022: £1,971 (54% increase). January 2023: £4,279 (peak).
The 2024-2026 situation (where we are now):
Wholesale gas prices stabilized and fell from February 2025 onwards. January 2026 price cap: £1,758, only 0.2% increase from previous quarter. But bills aren’t returning to 2021 levels (£1,277 average) because of structural cost increases that persist regardless of wholesale prices.
What’s keeping bills elevated:
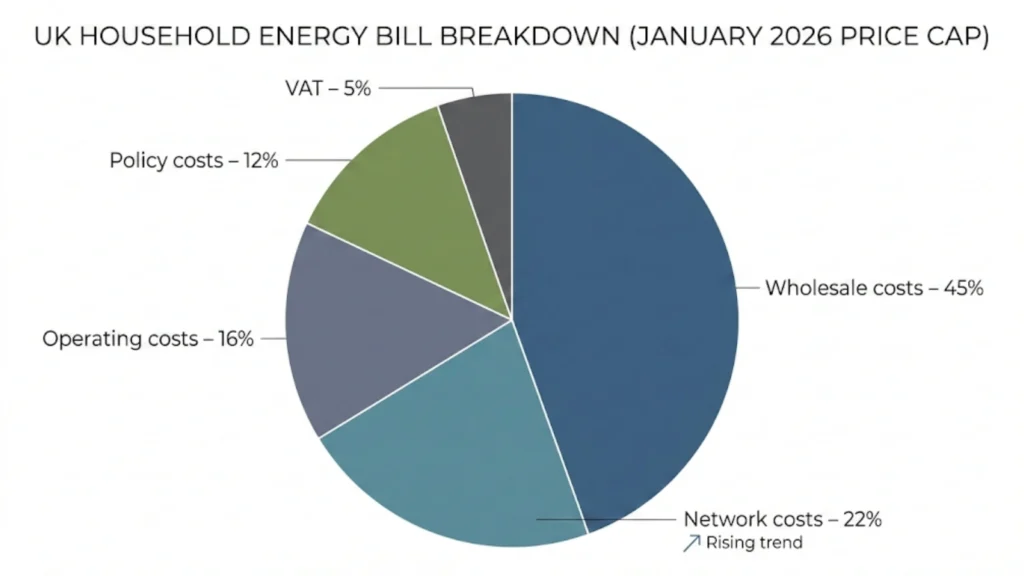
Network upgrade costs: Distribution Network Operators (DNOs) are reinforcing the grid for widespread EV charging and heat pump installation. These costs appear as rising standing charges (now 20-30% of typical bills). Ofgem-approved spending under RIIO-ED2 framework is passed directly to consumers.
Policy costs: Government schemes (ECO4, Warm Homes Plan) funded partially through bill levies. Carbon pricing via UK Emissions Trading Scheme adds cost to fossil fuel generation. Renewables integration and grid balancing services create ongoing operational expenses.
Supplier cost recovery: Many suppliers are still recouping losses from 2021-2023 market collapses when wholesale prices exceeded the price cap. This manifests as higher operating costs and reduced competition.
The pattern: Wholesale volatility caused the spike. Infrastructure and policy costs prevent full price drops. Bills in 2026 reflect transition costs toward electrification and net-zero, not just commodity markets.
What Households Can Actually Do (High Impact vs Marginal)
Not all energy-saving actions deliver equal returns. Let’s be specific about what works.
High Impact: Structural Fabric Improvements
Loft and cavity wall insulation:
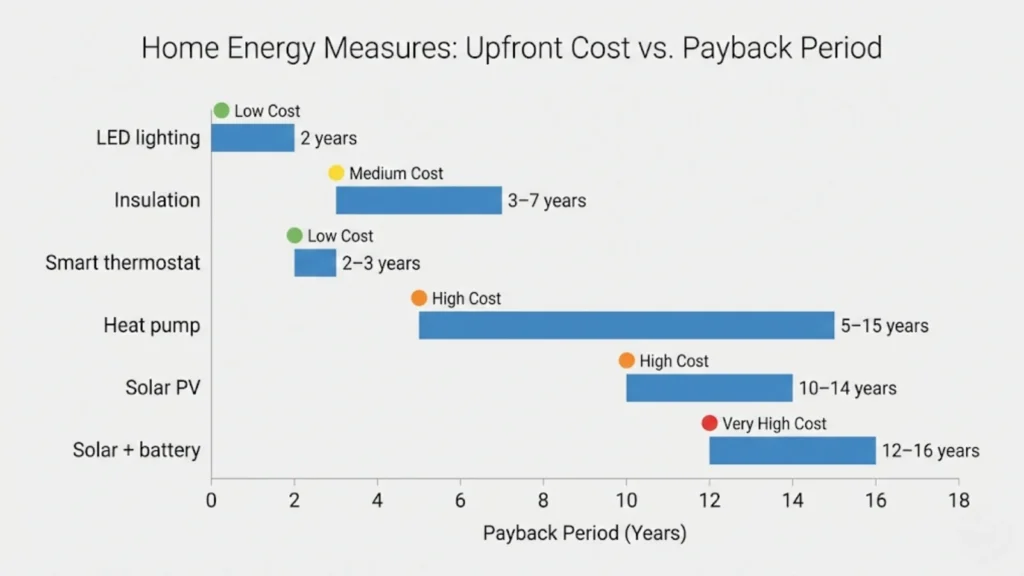
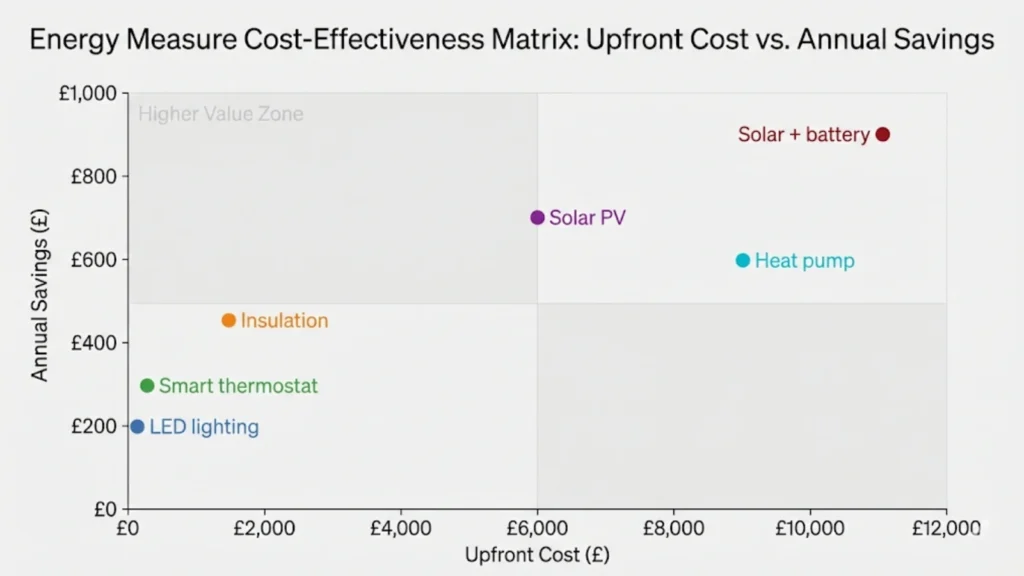
Saves: £200-£300 annually for uninsulated or poorly insulated homes. Cost: £500-£900 for loft, £1,500-£5,000 for cavity walls depending on property size. Payback: 3-7 years. Evidence: Energy Saving Trust standardized figures, verified through ECO4 scheme installations (949,800 measures delivered).
Worth it if: Your home lacks insulation or has inadequate original insulation. Marginal if: You already have 270mm+ loft insulation and filled cavity walls.
LED lighting (whole home replacement):
Saves: £50-£80 annually on lighting costs (10-20% of total lighting spend). Cost: £100-£200 for complete home conversion. Payback: Under 2 years. Evidence: Consistent across multiple studies, minimal controversy.
Worth it: Almost universally. Even partially lit homes benefit from full conversion. Most “low-hanging fruit” is already picked for households, but new builds and recent movers often haven’t completed this.
High Impact: Heating System Optimization
Smart thermostats with zoning capability:
Saves: 10-15% on heating costs (typically £150-£250 annually for gas-heated homes). Cost: £150-£500 depending on system complexity. Installation often requires electrician for wiring multi-zone controls. Payback: 2-3 years.
Worth it if: You have different usage patterns in different parts of your home, or you’re often heating empty rooms. Less effective: Single-room flats or homes with open-plan layouts where zoning provides minimal benefit.
Boiler flow temperature reduction:
Saves: £50-£80 annually by setting combi boiler flow temperature to 55-60°C instead of default 70-80°C. Cost: Free (DIY adjustment). Payback: Immediate. Evidence: Energy Saving Trust guidance, though savings vary by boiler efficiency and usage patterns.
Caveat: May reduce hot water temperature. Requires manual adjustment. Not all households will notice savings depending on existing efficiency.
High Impact: Generation and Storage (High Upfront Cost)
Solar PV (4kWp typical domestic system):
Saves: £400-£600 annually through self-consumption and export payments under Smart Export Guarantee (SEG). Cost: £5,000-£7,000 installed. Payback: 10-14 years without battery, improving as retail electricity prices remain elevated.
"Solar PV without battery storage means you're only using about 30% of what you generate; the rest goes to the grid at export rates much lower than what you pay for imported electricity. Adding a battery increases self-consumption to 70-80%, but that's an additional £4,000-£5,000 on top of solar costs. The payback calculation changes significantly."
Thomas Jevons, Head of Training
Solar + Battery storage (combined system):
Saves: £700-£1,000 annually through maximized self-consumption (70-80% of generated power used). Cost: £9,000-£12,000 for combined system (4kWp solar + 5kWh battery). Payback: 12-16 years at current prices.
Worth it if: You’re planning long-term home ownership (10+ years), have south/southwest-facing roof, and use electricity during daylight hours. Less compelling: If you’re on time-of-use tariffs that make overnight charging cheap, or if you’re planning to move within 5-7 years.
Heat pumps (via Warm Homes Plan):
Saves: £200-£500 annually compared to gas boilers for well-insulated homes (highly variable based on existing heating efficiency). Cost: £8,000-£14,000 installed, minus £7,500 Boiler Upgrade Scheme grant (£500-£6,500 net cost). Payback: 5-15 years depending on existing system and grant amount.
Worth it if: You have good insulation (EPC rating C or above preferred), large radiators or underfloor heating, and high heating costs. Less suitable: Poorly insulated homes where running costs may not drop sufficiently, or homes with adequate modern gas boilers where payback extends beyond 20 years.
Marginal Impact: Behavioral and Small Tech
Standby power reduction:
Saves: £20-£40 annually by switching off vampire loads (TVs, consoles, chargers left plugged in). Cost: Free or minimal (smart plugs: £5-£15 each). Evidence: Genuine but much smaller than a decade ago; modern electronics have lower standby consumption.
Lowering thermostat by 1°C:
Saves: Approximately 10% on heating costs (£100-£150 annually for typical gas-heated home). Cost: Free. Evidence: Widely cited, though actual savings depend on starting temperature, home insulation, and behavioral consistency.
Worth noting: This is behavioral, not structural. Savings disappear if habits revert.
The Electrician's Role in Energy Efficiency (Beyond Basic Wiring)
Electricians are shifting from “fault finding” to “system integration” as homes electrify. Electricians with retrofit and renewable energy qualifications command premium wages compared to general domestic work, with regional variations particularly strong in areas with major infrastructure projects like the West Midlands.
What electricians actually contribute:
Load balancing and circuit optimization: Adding EV chargers or heat pumps to existing electrical systems without upgrading consumer units or service heads can cause overloads, nuisance tripping, or fire risk. Electricians assess total load, upgrade consumer units (often from 60A to 100A service), and balance circuits to prevent electrical infrastructure becoming the bottleneck.
Smart control installation and programming: While homeowners can install basic smart plugs, professional smart thermostats with multi-zone controls require wiring expertise. Incorrect installation can cause voltage drop, inefficient heating control, or system malfunctions that negate efficiency gains.
Solar PV and battery integration: Connecting generation and storage to your home’s electrical system requires understanding AC/DC conversion, isolation, export limitation, and integration with existing circuits. MCS certification (Microgeneration Certification Scheme) required for grid connection approval and SEG payments.
Voltage optimization: Installing units that regulate incoming grid voltage (often 240V+) down to 220V reduces resistive waste and extends appliance lifespan. Savings are real but modest (£50-£100 annually on £400-£600 installation). Value is in cumulative effect and appliance protection, not dramatic bill cuts.
EV charger installation: Home EV chargers (7kW typical) require dedicated circuits, often with load management to prevent exceeding service capacity when multiple high-draw appliances operate simultaneously. Professional installation ensures compliance with BS 7671 and prevents electrical issues.
When you don’t need an electrician:
Basic LED bulb replacement. Plug-in smart meter displays (though installation of smart meters themselves requires qualified engineers). Draught-proofing, loft insulation (unless electrical wiring needs upgrading for safety). Simple plug-in timers or standby savers.
Realistic Payback and Cost-Effectiveness (The Numbers That Matter)
Marketing claims versus evidence-based reality.
Measures with strong evidence and reasonable payback:
Insulation (cavity wall and loft): Evidence: ECO4 scheme data shows consistent £200-£300 annual savings for previously uninsulated homes. Payback: 3-7 years depending on starting condition and installation cost. Lifetime savings: £3,000-£6,000 over 20-year insulation lifespan.
LED lighting: Evidence: Universally supported, minimal controversy. Payback: Under 2 years. Lifetime savings: £500-£1,000+ over bulb lifetimes (15-25 years).
Smart thermostats with zoning: Evidence: Energy Saving Trust estimates 10-15% heating cost reduction. Payback: 2-3 years. Caveat: Requires proper programming; many households don’t optimize settings, reducing realized savings.
Measures with longer payback requiring careful assessment:
Solar PV: Evidence: Strong for generation output, but payback heavily dependent on self-consumption patterns, export tariff rates, and retail electricity prices. Payback: 10-14 years without battery, 12-16 years with battery. Risk: Inverter replacement (typically 10-12 years) adds £1,000-£1,500 cost mid-life, extending payback.
Heat pumps: Evidence: Highly variable. Well-insulated homes with low flow-temperature heating systems show £200-£500 annual savings versus gas. Poorly insulated homes may see minimal savings or even cost increases. Payback: 5-15 years with £7,500 government grant; without grant, payback often exceeds 20 years. The growing demand for retrofit electricians reflects the skilled workforce needed for national electrification targets, with pay structures rewarding those who gain specialist certifications in renewable energy and heat pump technologies.
Measures with marginal returns:
Voltage optimization: Saves £50-£100 annually on £400-£600 installation. Payback: 5-10 years. Value is cumulative (appliance longevity, power quality) rather than dramatic bill reduction.
Standby power elimination: Saves £20-£40 annually. If using smart plugs (£5-£15 each), payback is reasonable, but absolute savings are small.
What affects payback calculations:
Usage patterns: High energy users see faster payback. Light users may never recover costs on expensive measures. Tariff structure: Time-of-use tariffs improve payback for storage and smart controls. Light users on standard tariffs benefit less. Installation quality: Poor installation of heat pumps, solar systems, or smart controls can halve expected efficiency gains. Home characteristics: Insulation level, existing heating system efficiency, roof orientation, available space for equipment.
Common Myths That Cost People Money
Let’s address misconceptions that lead to poor decisions or wasted spending.
Myth: “Just switching energy suppliers will solve high bills.” Reality: The January 2026 price cap limits tariff variation to approximately £50-£100 between cheapest and most expensive suppliers. Switching helps but doesn’t address underlying consumption. Structural efficiency improvements save multiples of what switching delivers.
Myth: “Smart meters automatically reduce your bills.” Reality: Smart meters provide real-time usage data and enable time-of-use tariffs. They don’t reduce consumption automatically. Savings require behavioral changes or load-shifting strategies based on the data. Average household savings from smart meter installation alone: minimal unless paired with actions.
Myth: “Leaving heating on low all day saves money compared to heating on-demand.” Reality: For typical UK housing stock (cavity wall, loft insulation, not high-thermal-mass concrete), heating continuously wastes energy. You’re compensating for heat loss constantly rather than heating as needed. Exception: Very well-insulated passive houses or high-thermal-mass buildings may benefit from consistent low temperature.
Myth: “Energy-saving plugs reduce power consumption.” Reality: These devices are scams. They claim to “reduce reactive power” or “stabilize voltage” but don’t reduce real power consumption (kW) that determines your bill. Trading Standards regularly warns against these fraudulent products.
Myth: “All electricians will double your savings on efficiency measures.” Reality: Electricians enable measures (smart controls, EV chargers, solar integration) but don’t guarantee specific savings. Realized savings depend on the measures implemented, installation quality, and household usage patterns. Proper electrical work ensures safety and enables efficiency; it doesn’t automatically multiply savings.
Myth: “Insulation isn’t worth it because it takes too long to pay back.” Reality: Cavity wall and loft insulation for uninsulated homes typically pays back in 3-7 years, then continues delivering savings for 20+ years. Cumulative lifetime savings: £3,000-£6,000. This is one of the most cost-effective interventions available.
Myth: “Behavioral changes don’t make a difference.” Reality: While less impactful than structural measures, consistent behavioral changes (thermostat management, turning off unused appliances, using appliances during off-peak on time-of-use tariffs) can save £100-£200 annually with zero upfront cost. The challenge is consistency, not effectiveness.
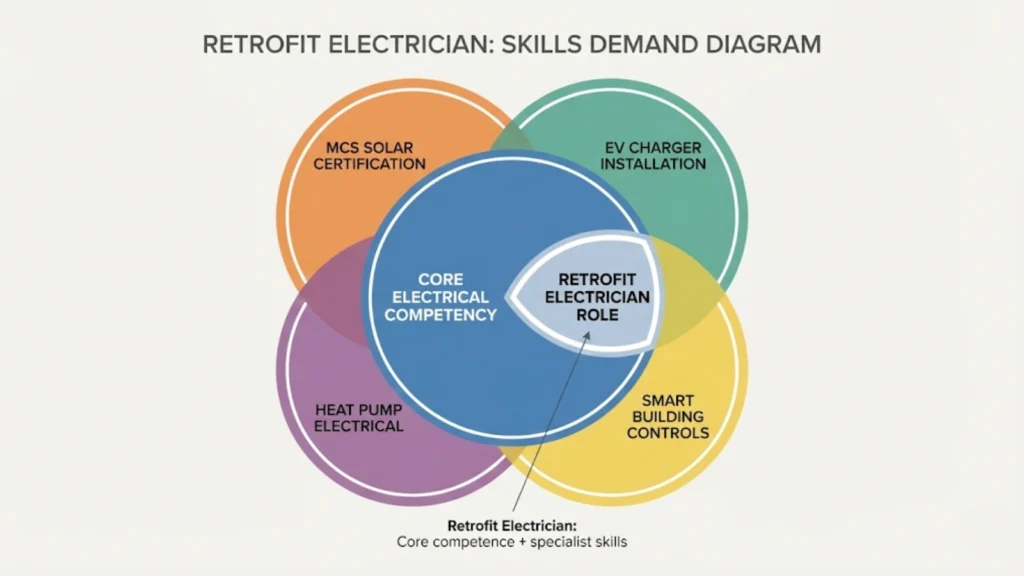
The Retrofit Electrician Opportunity (Why Employers Want These Skills)
The Warm Homes Plan and electrification targets are creating sustained demand for specific electrical skills.
What’s driving demand:
Government commitment to upgrade millions of homes with heat pumps, solar PV, and improved insulation by 2030. ECO4 scheme extended, requiring qualified installers for scheme-funded work. Projections: 400,000 clean energy jobs by 2030, substantial portion requiring electrical expertise.
Specific skills employers filter for:
MCS (Microgeneration Certification Scheme): Required for legal grid connection of solar PV and receiving SEG export payments. Electricians with MCS solar certification can charge premium rates.
Level 3 Award in Domestic, Commercial and Industrial Electric Vehicle Charging: Essential for EV charger installation work. Growing requirement as EV adoption increases and on-street/commercial charging expands.
Heat pump electrical interface competency: Understanding electrical requirements for air-source and ground-source heat pumps, including control system wiring, load management, and integration with existing heating controls.
Smart building controls: Proficiency in BMS (Building Management Systems), KNX protocols, or other smart home integration systems. Particularly valuable for commercial retrofit work. Employers are specifically looking for electricians who can demonstrate competency in retrofit and renewable technologies through recognized certifications rather than just general installation experience.
"Electricians with proper retrofit qualifications—MCS solar, heat pump competency, EV charger certification—are earning £40,000-£50,000 in the West Midlands on commercial energy efficiency projects. That's £8,000-£12,000 more than general domestic work, but you need the qualifications first, not just experience."
Joshua Jarvis, Placement Manager
Regional demand patterns:
West Midlands shows particularly strong demand due to infrastructure projects (HS2, Birmingham Smithfield) requiring electrical contractors with retrofit capability. London and South East: High retrofit demand for domestic properties meeting EPC upgrade requirements. Scotland: Strong heat pump adoption driving demand for electricians with heat pump electrical competency.
The skills gap:
Current electrical training produces general domestic electricians. The market needs specialists in renewable integration, energy management systems, and whole-home electrification load calculations. This gap creates opportunity for electricians willing to upskill in specific retrofit technologies.
What Actually Makes Sense for Most Households
Forget the hype. Here’s the practical framework.
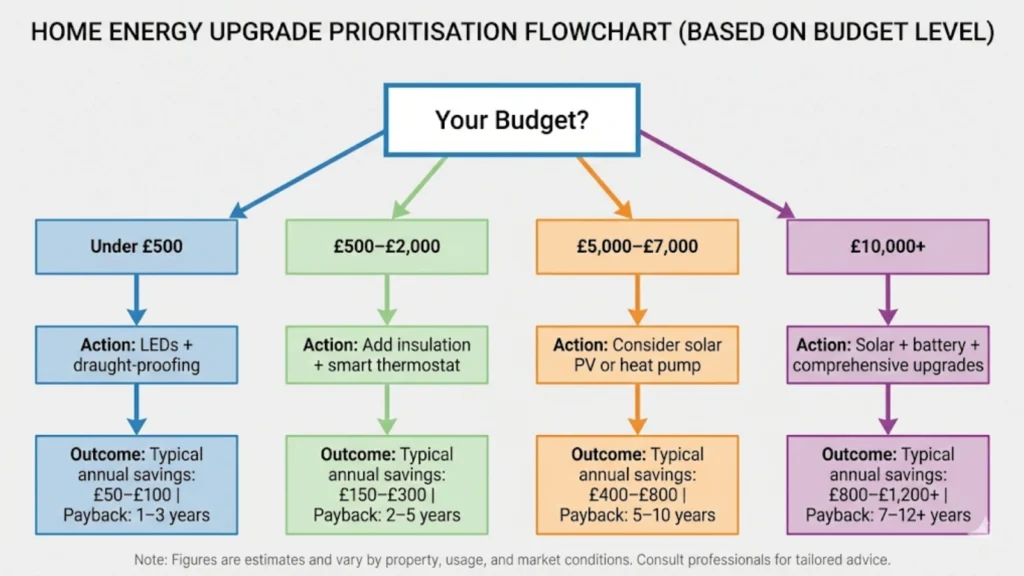
If your budget is under £500:
LED lighting throughout (if not already done). Draught-proofing (DIY or low-cost professional). Boiler flow temperature reduction (free DIY). Smart plugs for high-standby devices if desired (marginal gain but low cost).
Expected savings: £100-£200 annually. Payback: Under 2 years for LEDs and draught-proofing; immediate for flow temperature change.
If your budget is £500-£2,000:
Loft insulation (if inadequate or missing). Smart thermostat with zoning capability. Cavity wall insulation assessment (may need higher budget if work required).
Expected savings: £250-£400 annually depending on starting condition. Payback: 3-7 years.
If your budget is £5,000-£7,000 and you own long-term:
Solar PV (4kWp system) if you have suitable south/southwest-facing roof and daytime electricity usage. Heat pump consideration if you have good insulation and existing system is old/inefficient (budget includes £7,500 grant).
Expected savings: £400-£600 annually for solar; £200-£500 annually for heat pump (highly variable). Payback: 10-15 years.
If your budget is £10,000+ and you’re committed to long-term ownership:
Solar PV + battery storage for maximum self-consumption. Heat pump if suitable, potentially with solar to offset increased electricity usage. Comprehensive electrical system upgrade to support whole-home electrification (upgraded consumer unit, potentially upgraded service head).
Expected savings: £700-£1,000 annually. Payback: 12-16 years for solar+battery; variable for heat pump depending on existing system.
What to prioritize regardless of budget:
Insulation first. You can’t efficiently heat or cool a poorly insulated home. No amount of smart technology or renewable generation compensates for fabric energy loss.
LED lighting second. Cheapest, fastest payback.
Then heating controls. Smart thermostats with zoning provide strong returns for most households.
Only then consider generation/storage. These are long-term investments that work best when building fabric is already efficient.
Ready to Understand What Actually Reduces Your Bills?
Call us on 0330 822 5337 to discuss which energy efficiency pathways make sense for your circumstances, how electrical upgrades enable efficiency improvements, and why retrofit electrician skills create career opportunities in the clean energy transition.
What we’re not going to tell you:
- That any single measure will cut your bills by 50%
- That smart meters automatically save you money without behavioral changes
- That all electricians have retrofit qualifications (most don’t, yet)
- That you should invest in solar+battery without first addressing insulation
What we will tell you:
- Realistic payback periods for major investments (10-16 years for solar+battery)
- Which measures deliver quick returns (LEDs, insulation, smart thermostats)
- Why electricians are essential for safe electrification but not all upgrades
- How retrofit qualifications create £40,000-£50,000 earning potential in West Midlands
- The difference between marginal gains (standby reduction) and structural improvements (insulation, generation)
No overselling energy-saving gadgets. No misleading payback claims. Just honest guidance on what reduces bills structurally versus what just sounds impressive.
References
Primary Official Sources
- Ofgem Price Cap Updates (January 2026): https://www.ofgem.gov.uk/news/changes-energy-price-cap-between-1-january-and-31-march-2026
- Energy UK Price Cap Explainer: https://www.energy-uk.org.uk/publications/energy-uk-explains-january-2026-price-cap
- DESNZ Energy Trends and ECO4 Data: https://www.gov.uk/government/consultations/extending-the-eco4-end-date/outcome/extending-the-eco4-end-date-government-response-html
- UK Government Warm Homes Plan: https://www.gov.uk/government/news/families-to-save-in-biggest-home-upgrade-plan-in-british-history
- National Audit Office ECO Evaluation: https://www.nao.org.uk/reports/energy-efficiency-installations-under-the-energy-company-obligation
Energy Efficiency and Technical Standards
- IET Wiring Regulations BS 7671 (Part 8: Energy Efficiency): https://electrical.theiet.org/bs-7671/
- MCS (Microgeneration Certification Scheme): https://mcscertified.com/
- BEAMA Voltage Optimisation Guide: https://www.beama.org.uk/
Market Analysis and Labour Demand
- Nesta Budget Impact on Bills: https://www.nesta.org.uk/blog/what-does-the-budget-mean-for-energy-bills
- IFS Household Energy Efficiency Analysis: https://ifs.org.uk/journals/household-energy-efficiency-uk
- ECA Net Zero Commentary: https://www.eca.co.uk/taking-action/net-zero
Retrofit and Skills Demand
- Cavendish Professionals Construction Demand 2026: https://www.cavendishprofessionals.com/in-demand-construction-roles-2026
- LinkedIn Clean Energy Jobs Analysis: https://www.linkedin.com/posts/vince-bartal-ba2ab0128_energytransition-cleanenergyjobs-activity-7419298386220150784
- Edie Net Sustainability Careers Report: https://www.edie.net/sustainability-careers-buck-wider-hiring-slowdown-in-uk-jobs-market
Consumer Guidance
- Smart Energy GB Smart Meter Information: https://www.smartenergygb.org/
- Which? Energy Efficiency Advice: https://www.which.co.uk/reviews/saving-energy-in-the-home
Note on Accuracy and Updates
Last reviewed: 30 January 2026. This page is maintained; we correct errors and refresh sources as price cap levels, efficiency scheme details, and retrofit qualification requirements evolve. January 2026 price cap (£1,758), Warm Homes Plan details, and clean energy jobs projections reflect current government data. Payback calculations use Energy Saving Trust standardized figures but actual results vary by household usage, tariff structure, and installation quality. Next review scheduled following April 2026 price cap announcement and any significant changes to ECO4 or renewable energy scheme funding.
FAQs
Essential skills for an electrician in 2026 refer to the practical ability to carry out work safely and competently under real site conditions, not just holding certificates. Under BS 7671 (18th Edition) and EAS 2024, this means hands-on proficiency in installation, inspection, testing, and fault finding developed through supervised site experience.
Employers expect these skills to be demonstrated in NVQ portfolios and AM2 assessments, where theory must translate into accurate, compliant work. Without them, electricians risk site removal due to unsafe practices such as poor isolation or non-compliant installations. Competence also includes judgement when working on older or mixed systems, and consistent compliance with EAWR 1989 to protect both the electrician and others on site.
Insulation makes the biggest difference to energy bills by reducing heat loss structurally, outperforming heating controls or tariff switching over the long term. Fabric measures such as loft or wall insulation permanently cut demand, whereas heating controls mainly deliver marginal behavioural savings.
Switching tariffs can offer quick reductions, but results depend on market conditions and rarely match insulation’s lasting impact. Evidence from Energy Saving Trust and Uswitch shows structural upgrades typically save more annually than controls or tariff changes alone.
What to check: your home’s EPC rating, loft and wall insulation levels, available tariffs via comparison sites.
Quick wins under £500 include draught-proofing, LED lighting upgrades, hot water cylinder jackets, and pipe lagging. These reduce energy loss quickly with short payback periods.
Evidence from Energy Saving Trust and BBC guidance shows these measures outperform gimmicks like “energy-saving plugs,” which do not reduce billed kWh. Many improvements are DIY, but electrical work should always be safe and compliant.
What to check: draught sources around doors and windows, bulb types in use, hot water and pipe insulation status.
Fabric first prioritises improving the building envelope, insulation, airtightness, and glazing, before adding technology. It beats most smart gadgets by reducing energy demand at source, rather than tweaking behaviour.
Studies in retrofit research show fabric measures deliver greater comfort, emissions reductions, and long-term bill savings than technology alone. Smart devices can complement good fabric but rarely compensate for poor insulation.
What to check: insulation depth, air leakage points, EPC fabric upgrade recommendations.
Smart thermostats and meters can save money through better control and awareness, but real-world savings are typically modest. Research from the Behavioural Insights Team and Centrica suggests average savings around three percent, varying by household behaviour.
They work best in already efficient homes and with engaged users. While not hype, they are marginal improvements rather than structural fixes.
What to check: heating system compatibility, availability of time-of-use tariffs, independent reviews on real savings.
Solar PV reduces bills when systems are well-sized, south-facing, minimally shaded, and matched to household usage. Self-consumption delivers the biggest savings, with exports paid via the Smart Export Guarantee (SEG).
It disappoints where roofs are poorly oriented, heavily shaded, or household usage is low, leading to excess exports at low SEG rates. MCS-certified installation and realistic payback expectations are key.
What to check: roof orientation and shading, annual electricity usage, MCS-accredited installers.
Home batteries can be worthwhile for households with solar PV and time-of-use tariffs, storing excess energy for peak periods. Falling battery prices have improved viability when self-use is maximised.
Avoid batteries if you do not have solar, are on flat tariffs, or plan to move soon. Upfront costs often outweigh benefits in these cases. Proper installation to BS 7671 is essential.
What to check: existing solar setup, tariff structure, battery compatibility and DNO requirements.
Heat pumps reduce bills when installed in well-insulated homes and correctly sized. Evidence from UK studies shows savings compared to gas boilers, especially with grants under the Boiler Upgrade Scheme.
They perform best in homes with high EPC ratings, low-temperature heating systems, and suitable tariffs. Poor insulation significantly reduces effectiveness.
What to check: insulation quality, EPC score, eligibility for Boiler Upgrade Scheme funding.
Electricians add value when installing or upgrading systems such as solar PV, heat pumps, EV chargers, batteries, and consumer units, ensuring safe and efficient operation under BS 7671.
They are unnecessary for simple marginal measures like changing bulbs or draught-proofing. Electrical work should always be undertaken by competent, certified professionals.
What to check: electrician certifications (NICEIC, MCS), need for consumer unit upgrades, BS 7671 compliance.
Households should prioritise fabric-first improvements before investing in heating systems or renewables. Reducing demand maximises the effectiveness of later technologies.
Use EPC recommendations and ECO funding eligibility to target the biggest weaknesses first. Avoid unproven gadgets that do not reduce actual kWh usage.
What to check: EPC report actions, ECO scheme eligibility, DNO approval for major electrical upgrades.


